The benefits of electrotherapy in physiotherapy: a complete and effective approach
Electrotherapy, an integral part of physiotherapy for many decades, is a technique that has demonstrated its effectiveness. Coming from the field of physiotherapy, it takes advantage of physical agents, notably electricity, to produce remarkable results. This approach can be used independently or in addition to other physiotherapy methods such as massage, as well as other forms of physiotherapy such as ultrasound therapy or shock wave treatment.

The benefits of shock wave treatment
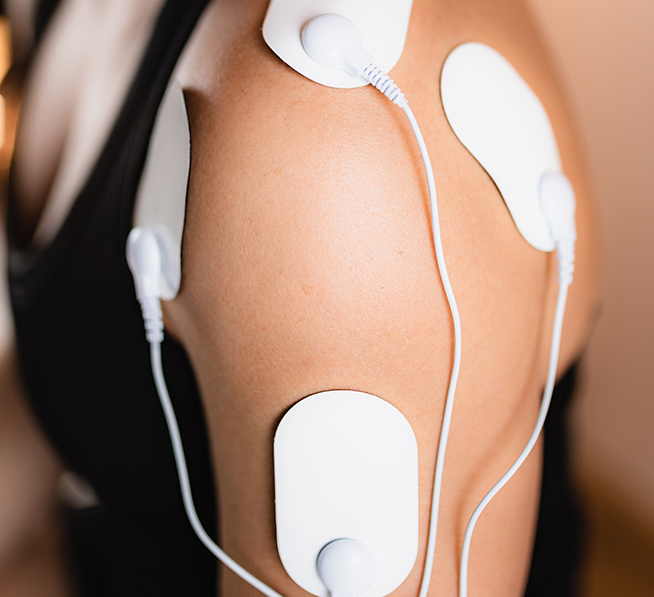
Electrotherapy, a versatile and effective method in physiotherapy, is recommended for various pathologies. Its ability to relieve pain and promote healing makes it a widely used approach in the field.
It is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals suffering from pain or muscle injuries. By acting on tissue regeneration, it significantly contributes to relieving pain. It is also effective in treating joint pain linked to sports injuries, aging or sudden movements, while promoting muscle strengthening and tissue toning.
Electrotherapy is also recommended for pain related to tendons and nerves. For example, it can soothe sciatic pain and contribute to the patient’s general well-being. Likewise, it is beneficial for lumbosciatalgia, cruralgia and cervico-brachial neuralgia.
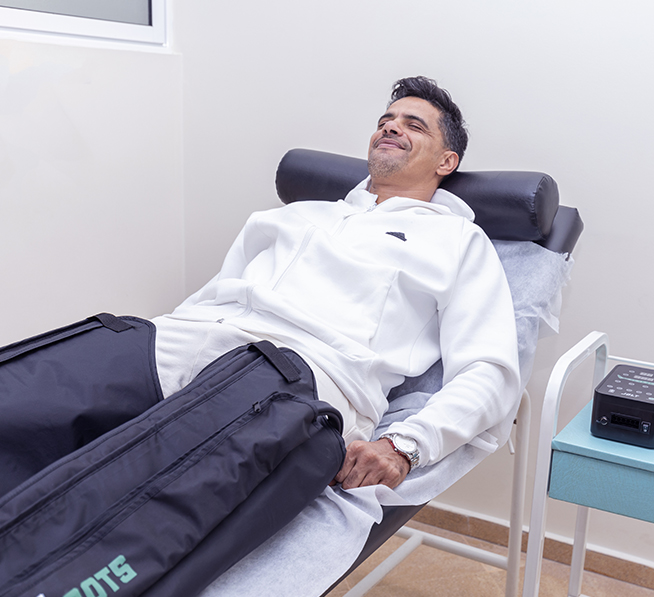
Improve blood and lymphatic circulation with Pressotherapy
Pressotherapy, a medical and paramedical technique, aims to stimulate blood and lymphatic circulation by applying pressure to the limbs of the body. This pressure is exerted not manually by a healthcare professional, but by machines in the form of wide boots, arm sleeves or abdominal belts. The patient remains lying down during therapy.
These devices, connected to an air compressor, have several pneumatic compartments. Depending on the program chosen, these compartments inflate to exert more or less pressure on the limbs. The pressure can be constant or sequential depending on the condition being treated.
A pressotherapy session generally lasts between 20 and 30 minutes and may be recommended by a general practitioner or physiotherapist.